def model(X_train, Y_train, X_test, Y_test, learning_rate = 0.0001,
num_epochs = 1500, minibatch_size = 32, print_cost = True):
"""
Implements a three-layer tensorflow neural network: LINEAR->RELU->LINEAR->RELU->LINEAR->SOFTMAX.
Arguments:
X_train -- training set, of shape (input size = 12288, number of training examples = 1080)
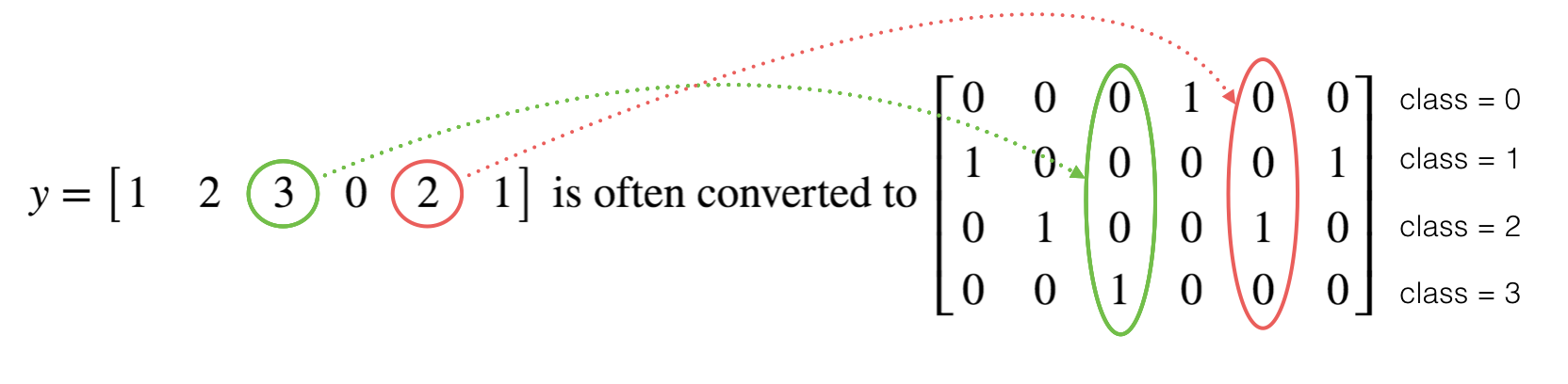
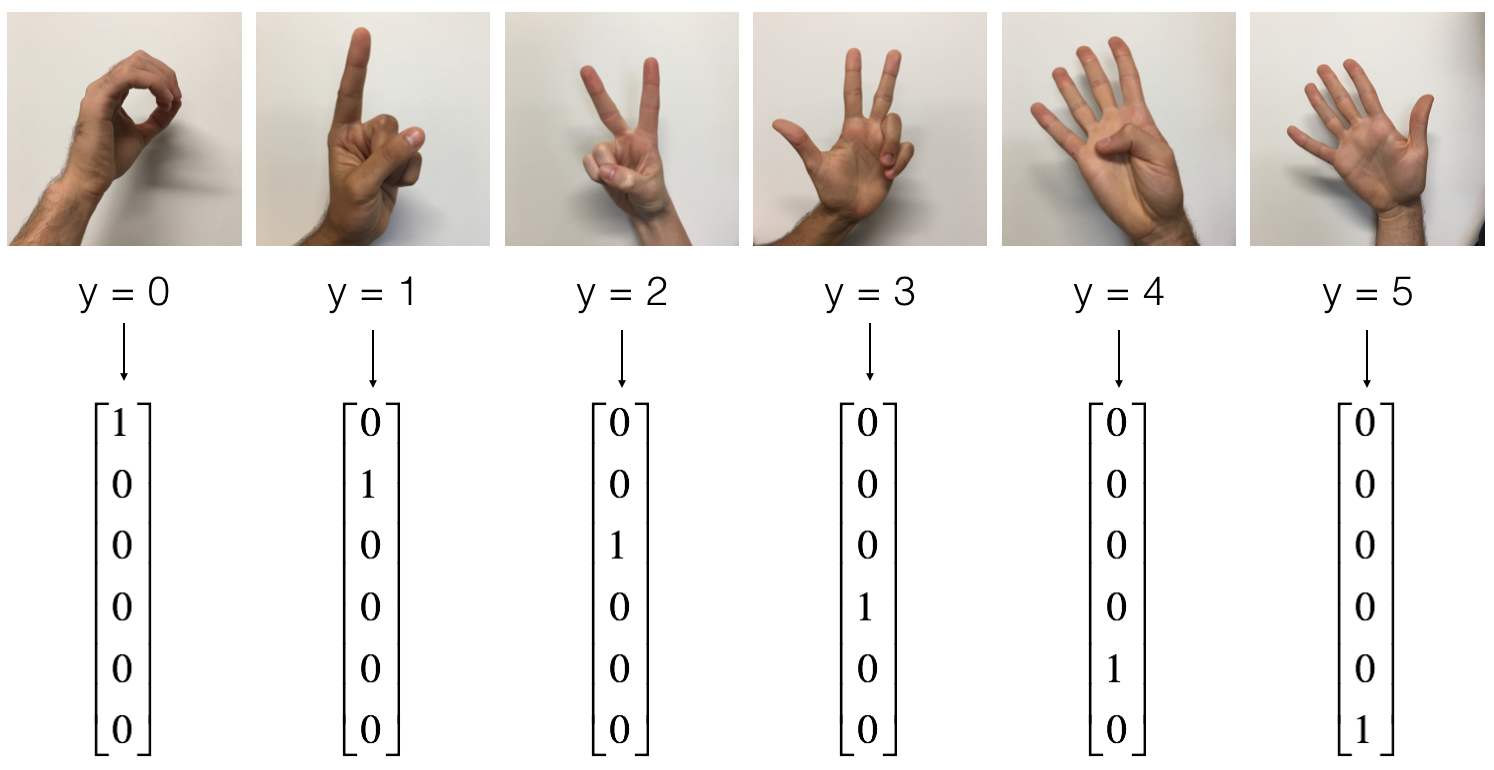
Y_train -- test set, of shape (output size = 6, number of training examples = 1080)
X_test -- training set, of shape (input size = 12288, number of training examples = 120)
Y_test -- test set, of shape (output size = 6, number of test examples = 120)
learning_rate -- learning rate of the optimization
num_epochs -- number of epochs of the optimization loop
minibatch_size -- size of a minibatch
print_cost -- True to print the cost every 100 epochs
Returns:
parameters -- parameters learnt by the model. They can then be used to predict.
"""
ops.reset_default_graph() # to be able to rerun the model without overwriting tf variables
tf.set_random_seed(1) # to keep consistent results
seed = 3 # to keep consistent results
(n_x, m) = X_train.shape # (n_x: input size, m : number of examples in the train set)
n_y = Y_train.shape[0] # n_y : output size
costs = [] # To keep track of the cost
# Create Placeholders of shape (n_x, n_y)
### START CODE HERE ### (1 line)
X, Y = create_placeholders(n_x, n_y)
### END CODE HERE ###
# Initialize parameters
### START CODE HERE ### (1 line)
parameters = initialize_parameters()
### END CODE HERE ###
# Forward propagation: Build the forward propagation in the tensorflow graph
### START CODE HERE ### (1 line)
Z3 = forward_propagation(X, parameters)
### END CODE HERE ###
# Cost function: Add cost function to tensorflow graph
### START CODE HERE ### (1 line)
cost = compute_cost(Z3, Y)
### END CODE HERE ###
# Backpropagation: Define the tensorflow optimizer. Use an AdamOptimizer.
### START CODE HERE ### (1 line)
optimizer = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate = learning_rate).minimize(cost)
### END CODE HERE ###
# Initialize all the variables
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
# Start the session to compute the tensorflow graph
with tf.Session() as sess:
# Run the initialization
sess.run(init)
# Do the training loop
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
epoch_cost = 0. # Defines a cost related to an epoch
num_minibatches = int(m / minibatch_size) # number of minibatches of size minibatch_size in the train set
seed = seed + 1
minibatches = random_mini_batches(X_train, Y_train, minibatch_size, seed)
for minibatch in minibatches:
# Select a minibatch
(minibatch_X, minibatch_Y) = minibatch
# IMPORTANT: The line that runs the graph on a minibatch.
# Run the session to execute the "optimizer" and the "cost", the feedict should contain a minibatch for (X,Y).
### START CODE HERE ### (1 line)
_ , minibatch_cost = sess.run([optimizer, cost], feed_dict={X: minibatch_X, Y: minibatch_Y})
### END CODE HERE ###
epoch_cost += minibatch_cost / minibatch_size
# Print the cost every epoch
if print_cost == True and epoch % 100 == 0:
print ("Cost after epoch %i: %f" % (epoch, epoch_cost))
if print_cost == True and epoch % 5 == 0:
costs.append(epoch_cost)
# plot the cost
plt.plot(np.squeeze(costs))
plt.ylabel('cost')
plt.xlabel('iterations (per fives)')
plt.title("Learning rate =" + str(learning_rate))
plt.show()
# lets save the parameters in a variable
parameters = sess.run(parameters)
print ("Parameters have been trained!")
# Calculate the correct predictions
correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(Z3), tf.argmax(Y))
# Calculate accuracy on the test set
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction, "float"))
print ("Train Accuracy:", accuracy.eval({X: X_train, Y: Y_train}))
print ("Test Accuracy:", accuracy.eval({X: X_test, Y: Y_test}))
return parameters